1.介绍
Spring是通过任务执行器(TaskExecutor)来实现多线程和并发编程,使用ThreadPoolTaskExecutor来创建一个基于线城池的TaskExecutor。在使用线程池的大多数情况下都是异步非阻塞的。我们配置注解@EnableAsync可以开启异步任务。然后在实际执行的方法上配置注解@Async上声明是异步任务。
2.操作步骤
2.1 使用@EnableAsync开启Springboot对于异步任务的支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.zhu.common;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class CommonApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CommonApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
2.2 配置线程池
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package com.zhu.common.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfiguration {
@Bean("demoExecutor")
public Executor doSomethingExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("demo-exe-");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
|
2.3 使用@Async注解实现异步调用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.zhu.common.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncDemoService {
@Async("demoExecutor")
public void showIndex(Integer index){
log.info("The index is {}",index);
}
}
|
2.4 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| package com.zhu.common;
import com.zhu.common.service.AsyncDemoService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = CommonApplication.class)
public class AsyncTest {
@Autowired
AsyncDemoService asyncDemoService;
@Test
public void testAsync() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
asyncDemoService.showIndex(i);
}
}
}
|
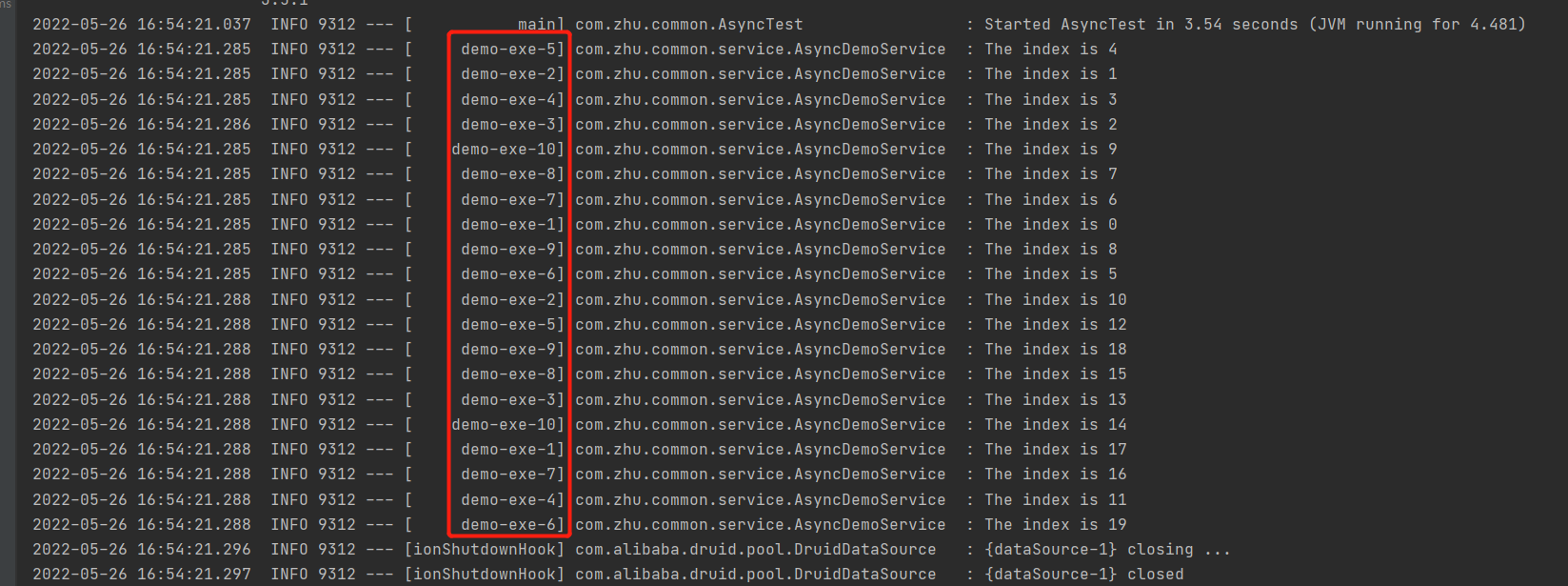
测试结果:
3 注意事项
@Async注解会在以下几个场景失效
- SpringBoot应用中没有添加@EnableAsync注解
- 异步方法使用static关键词修饰
- 异步类不是一个Spring容器的bean(一般使用注解@Component和@Service,并且能被Spring扫描到)
- 在同一个类中,一个方法调用另外一个有@Async注解的方法,注解不会生效。原因是@Async注解的方法,是在代理类中执行的。
异步方法返回值
异步方法使用注解@Async的返回值只能为void或者Future及其子类,当返回结果为其他类型时,方法还是会异步执行,但是返回值都是null。
