1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
| package com.zhu.common.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
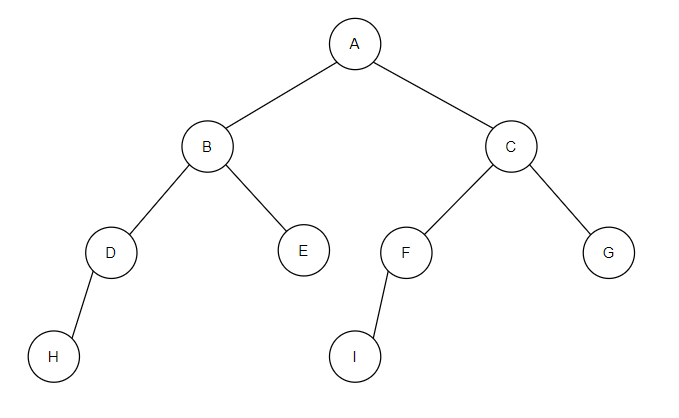
public class BinaryTreeTest {
private static List<BinNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
private static class BinNode {
private Object element;
private BinNode lChild;
private BinNode rChild;
public BinNode(Object element, BinNode lChild, BinNode rChild) {
this.element = element;
this.lChild = lChild;
this.rChild = rChild;
}
}
public static BinNode init() {
BinNode h = new BinNode("H", null, null);
BinNode i = new BinNode("I", null, null);
BinNode d = new BinNode("D", h, null);
BinNode e = new BinNode("E", null, null);
BinNode f = new BinNode("F", i, null);
BinNode g = new BinNode("G", null, null);
BinNode b = new BinNode("B", d, e);
BinNode c = new BinNode("C", f, g);
BinNode a = new BinNode("A", b, c);
return a;
}
public static void preOrder(BinNode node) {
list.add(node);
if (node.lChild != null) {
preOrder(node.lChild);
}
if (node.rChild != null) {
preOrder(node.rChild);
}
}
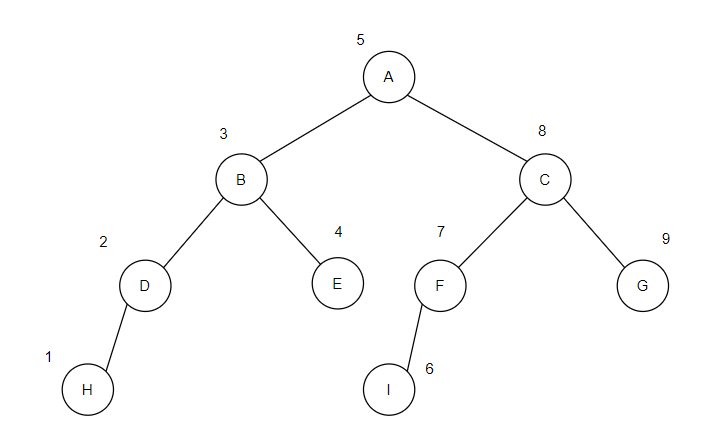
public static void inOrder(BinNode node) {
if (node.lChild != null) {
inOrder(node.lChild);
}
list.add(node);
if (node.rChild != null) {
inOrder(node.rChild);
}
}
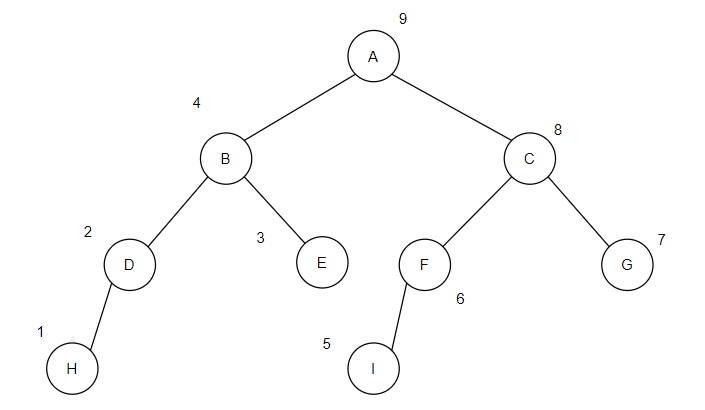
public static void postOrder(BinNode node) {
if (node.lChild != null) {
postOrder(node.lChild);
}
if (node.rChild != null) {
postOrder(node.rChild);
}
list.add(node);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinNode tree = init();
preOrder(tree);
System.out.println("先序遍历结果:");
list.forEach(n -> {
System.out.print(n.element + " ");
});
list.clear();
System.out.println();
inOrder(tree);
System.out.println("中序遍历结果:");
list.forEach(n -> {
System.out.print(n.element + " ");
});
list.clear();
System.out.println();
postOrder(tree);
System.out.println("后序遍历结果:");
list.forEach(n -> {
System.out.print(n.element + " ");
});
}
}
|